How Do I Roll Back the Kernel Version If I Mistakenly Upgrade the Kernel?¶
Scenarios¶
SDI, RAID, and IB hardware drivers of the BMS are related to the kernel. You are not advised to upgrade the kernel version.
If you have upgraded the kernel, perform the operations in this section. This section uses CentOS 7.2 as an example to describe how to set the BMS OS to start from the default kernel if you have upgraded the kernel.
Upgrade Scenario¶
Run the uname -a command to query the current kernel version.
[root@bms-centos ~]# uname -a Linux bms-centos 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Thu Nov 29 14:49:43 UTC 2018 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
Run the yum update kernel command to upgrade the kernel.
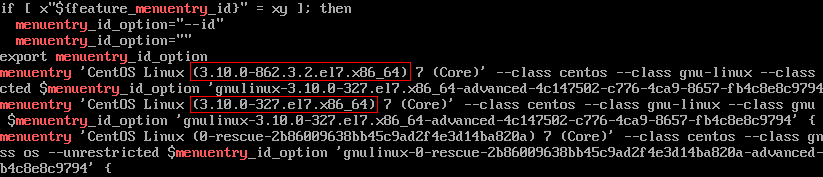
Run the cat /boot/grub2/grub.cfg |grep menuentry command to check the kernel information of the OS after the upgrade.
As shown in the following figure, 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64 is the default kernel version and 3.10.0-862.3.2.el7.x86_64 is the upgraded kernel version.
Emergency Settings After Kernel Upgrade¶
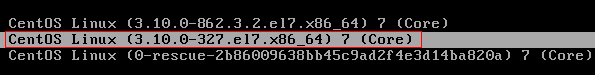
Run the following commands to set the original kernel version as the default startup kernel and verify the modification result:
grub2-set-default "CentOS Linux (3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64) 7 (Core)"
grub2-editenv list
[root@bms-centos ~]# grub2-editenv list saved_entry-CentOS Linux (3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64) 7 (Core)
After the verification is complete, restart the OS from the default kernel.
Run the uname -a command to check whether the kernel version is restored.