What Is APIG?¶
API Gateway (APIG) is your fully managed API hosting service. With APIG, you can build, manage, and deploy APIs at any scale to package your capabilities. With just a few clicks, you can integrate internal systems, monetize service capabilities, and selectively expose capabilities with minimal costs and risks. APIG helps you monetize service capabilities and reduce R&D investment, and enables you to focus on core enterprise services to improve operational efficiency.
To monetize your capabilities (services and data), you can open them up by creating APIs in APIG. Then you can provide the APIs for API callers using offline channels.
You can also obtain open APIs from APIG to reduce your development time and costs.
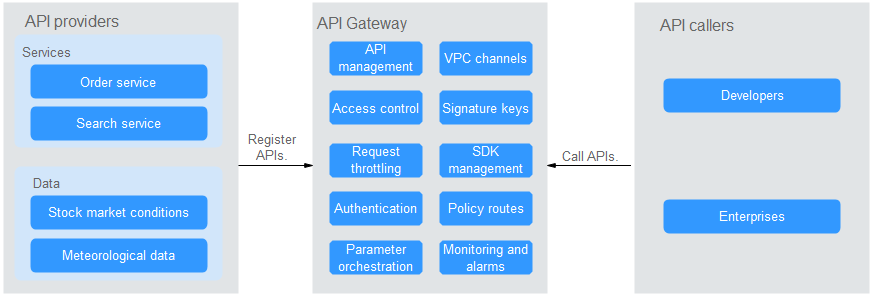
Figure 1 APIG architecture¶
Product Functions¶
API lifecycle management
The lifecycle of an API involves creating, publishing, removing, and deleting the API. API lifecycle management enables you to quickly and efficiently expose service capabilities.
Built-in debugging tool
With the built-in debugging tool, you can debug APIs using different HTTP headers and request bodies. This tool simplifies the API development process and reduces the API development and maintenance costs.
Version management
An API can be published in different environments. Publishing an API again in the same environment will override the API's previous version. APIG displays the publication history (including the version, description, date and time, and environment) of each API. You can roll back an API to any historical version to meet dark launch and version upgrade requirements.
Environment variables
Environment variables are manageable and specific to environments. Variables of an API will be replaced by the values of the variables in the environment where the API will be published. You can create variables in different environments to call different backend services using the same API.
Refined request throttling
For different service demands and user levels, you can control the frequency at which an API can be called by a user, app (credential), or IP address, ensuring that backend services can run stably.
Configure different request throttling limits with API path, query, and header parameters.
The throttling can be accurate to the second, minute, hour, or day.
Set throttling limits for excluded applications (credentials) and tenants.
Monitoring and alarms
APIG provides visualized, real-time API monitoring, and displays multiple metrics, including number of requests, invocation latency, and number of errors. The metrics help you understand the API usage, allowing you to identify potential service risks.
Security
Domain name access can be authenticated with TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2. mTLS two-way authentication is supported.
Access control policies limit API access from specific IP addresses or accounts. You can blacklist or whitelist certain IP addresses and accounts to access your APIs.
Circuit breaker policies protect your backend services through degradation if they are abnormal.
Identity authentication can be based on AK/SK, function-based custom authorizers, and tokens. APIG verifies your backend services via certificates and is verified by your backend services through signature keys.
VPC channels (load balance channels)
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) channels (load balance channels) can be created for accessing resources in VPCs and exposing backend services deployed in VPCs. VPC channels balance API requests to backend services.
Mock response
Mock backends simulate API responses for circuit breakers, service degradation, and redirection.