Creating a VPC Channel¶
Scenario¶
VPC channels allow services deployed in VPCs to be accessed through their subnets, lowering latency and balancing loads of backend services.
After creating a VPC channel, you can configure it for an API with an HTTP/HTTPS backend service. For example, six ECSs have been deployed in a VPC, and a VPC channel has been created to reach ECS 01 and ECS 04. APIG can access these two ECSs through the VPC channel.
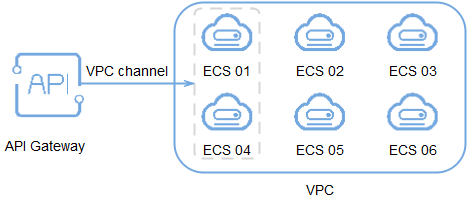
Figure 1 Accessing ECSs in a VPC channel through APIG¶
Note
Dedicated gateways support VPC channels with a private network load balancer.
Prerequisites¶
You have created a cloud server.
You have the VPC Administrator permission.
Creating a Fast Channel¶
Log in to the management console.
In the navigation pane, choose Dedicated Gateways. Then click Access Console in the upper right corner of a dedicated gateway.
In the navigation pane, choose API Publishing > VPC Channels.
Click Create VPC Channel, and set the parameters listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Parameters for creating a VPC channel¶ Parameter
Description
Name
VPC channel name.
Port
The host port of the VPC channel, that is, the port of the backend service.
Range: 1-65535.
Member Type
Select a method that you want to use to specify servers for the VPC channel. The member type is a one-time configuration and cannot be changed after you create the VPC channel.
Instance: Select cloud servers.
IP address: Specify cloud server IP addresses.
Routing Algorithm
The algorithm to be used to forward requests to cloud servers you select.
The following routing algorithms are available:
WRR: weighted round robin
WLC: weighted least connection
SH: source hashing
URI hashing
Protocol
The protocol used to perform health checks on cloud servers associated with the VPC channel. Options:
TCP
HTTP
HTTPS
Default value: TCP.
Path
The destination path for health checks.
Set this parameter only when Protocol is not set to TCP.
Check Port
The destination port for health checks.
By default, the port of the VPC channel will be used.
Healthy Threshold
The number of consecutive successful checks required for a cloud server to be considered healthy.
Range: 2-10. Default value: 2.
Unhealthy Threshold
The number of consecutive failed checks required for a cloud server to be considered unhealthy.
Range: 2-10. Default value: 5.
Timeout (s)
The timeout used to determine whether a health check has failed. Unit: s.
Range: 2-30. Default value: 5.
Interval (s)
The interval between consecutive checks. Unit: s.
Range: 5-300. Default value: 10.
Response Codes
The HTTP codes used to check for a successful response from a target.
Set this parameter only when Protocol is not set to TCP.
Click Next.
Click Select Cloud Server.
Select the cloud servers you want to add, and click OK.
Note
To ensure a successful health check and service availability, configure the security groups of the cloud servers to allow access from 100.125.0.0/16.
Click Finish.
Follow-Up Operations¶
Create an API for backend services deployed in a VPC to balance loads.