Creating an Environment Variable¶
You can define environment variables to allow an API to be called in different environments.
Environment variables are manageable and specific to environments. You can add variables in different environments to call different backend services using the same API.
For variables you define during API creation, you must create corresponding variables and values. For example, variable Path is defined for an API, and two variables with the same name are created and assigned values /Stage/test and /Stage/AA in environments 1 and 2, respectively. If the API is published and called in environment 1, the path /Stage/test is used. If the API is published and called in environment 2, the path /Stage/AA is used.
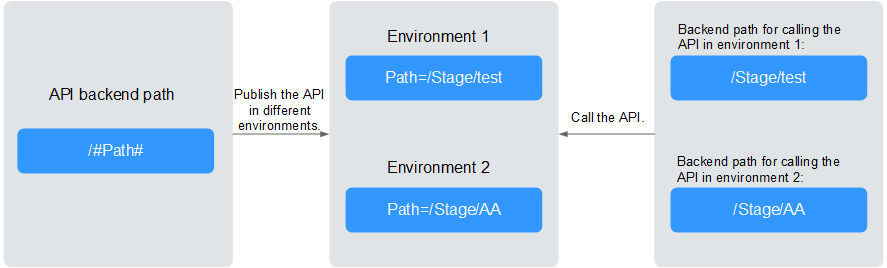
Figure 1 Use of environment variables¶
Procedure¶
Go to the APIG console.
Select a dedicated gateway at the top of the navigation pane.
Choose API Management > API Groups.
Click a group name.
Click the Group Information tab.
In the Environment Variables area, select an environment. If no environment is available, click Create Environment to create one.
Click Add Environment Variable and enter the variable information.
Important
Environment variable names and values will be displayed in plain text in API requests. Do not include sensitive information in the variable names and values.
Table 1 Adding an environment variable¶ Parameter
Description
Name
Variable name. Ensure that the name is the same as the name of the variable defined for the API.
Value
The path to be used in the selected environment.
Click OK.
Follow-Up Operations¶
After creating an environment variable, you can publish the API in the environment where the variable is located so that the API can be called.